SOA interview questions
Question 1. What Is Bpel?
Answer :
Within the enterprise, BPEL is used to standardize enterprise application integration as well as to extend the integration to previously isolated systems. Between enterprises, BPEL enables easier and more effective integration with business partners. BPEL stimulates enterprises to further define their business processes, which in turn leads to business process optimization, reengineering, and the selection of the most appropriate processes, thus further optimizing the organization.
Definitions of business processes described in BPEL do not affect existing systems, thereby stimulating upgrades. BPEL is the key technology in environments where functionalities are already or will be exposed via Web services. With increases in the use of Web services, the importance of BPEL will increase as well.
BPEL represents a convergence of two early workflow languages; Web Services Flow Language (WSFL) and XLANG. WSFL was designed by IBM and is based on the concept of directed graphs. XLANG, a block-structured language, was designed by Microsoft. BPEL combines both approaches and provides a rich vocabulary for description of business processes.
Question 2. What Is Oracle Jdeveloper?
Answer :
Oracle BPEL Process Manager provides support for using Oracle JDeveloper to graphically design BPEL processes.
Oracle JDeveloper is an integrated development environment (IDE) for building applications and Web services using Java, XML, and SQL standards. Oracle JDeveloper supports the entire development life cycle with integrated features for designing, coding, debugging, testing, profiling, tuning, and deploying applications. A visual and declarative development approach and the Oracle Application Development Framework (ADF) work together to simplify application development and reduce coding tasks.
Oracle JDeveloper uses BPEL as its native format. This means that processes built with Oracle JDeveloper are 100% portable. Oracle JDeveloper also enables you to view and modify the BPEL source without decreasing the usefulness of the tool.
You design BPEL processes by dragging and dropping elements (known as activities) into the process and editing their property pages. This eliminates the need to write BPEL code. You integrate BPEL processes with external services (known as partner links). You also integrate adapters and services such as workflows, transformations, notifications, sensors, worklist task management, and business rules with the process. Oracle JDeveloper can deploy the developed processes directly to Oracle BPEL Server. This facilitates the development and maintenance of BPEL processes.
Oracle BPEL Process Manager provides support for the following services and adapters in Oracle JDeveloper:
Transformations, workflows, worklists, notifications, sensors, and business rules
Technology adapters (file, FTP, database, AQ, JMS, MQ, and Oracle Applications)
Question 3. What Are Two Ways Of Combining Web Services?
Answer :
Web services can be combined in two ways:
Orchestration
Choreography
Question 4. Explain Orchestration And Choreography?
Answer :
In orchestration, which is usually used in private business processes, a central process (which can be another Web service) takes control of the involved Web services and coordinates the execution of different operations on the Web services involved in the operation. The involved Web services do not "know" (and do not need to know) that they are involved in a composition process and that they are taking part in a higher-level business process. Only the central coordinator of the orchestration is aware of this goal, so the orchestration is centralized with explicit definitions of operations and the order of invocation of Web services.
Choreography, in contrast, does not rely on a central coordinator. Rather, each Web service involved in the choreography knows exactly when to execute its operations and with whom to interact. Choreography is a collaborative effort focusing on the exchange of messages in public business processes. All participants in the choreography need to be aware of the business process, operations to execute, messages to exchange, and the timing of message exchanges.
Question 5. What Are Two Different Ways Of Describing Business Processes That Are Supported By Bpel?
Answer :
BPEL supports two different ways of describing business processes that support orchestration and choreography:
Executable processes allow you to specify the exact details of business processes. They follow the orchestration paradigm and can be executed by an orchestration engine.
Abstract business protocols allow specification of the public message exchange between parties only. They do not include the internal details of process flows and are not executable. They follow the choreography paradigm.
Question 6. List Of All Primitive Activities Supported By Bpel Business Process?
Answer :
Primitive activities represent basic constructs and are used for common tasks, such as the following:
Invoking other Web services.
Waiting for the client to invoke the business process by sending a message.
Generating a response for synchronous operations.
Manipulating data variables.
Indicating faults and exceptions.
Waiting for some time.
Terminating the entire process.
Question 7. What Is The Use Of Bpel Business Process?
Answer :
In a typical scenario, the BPEL business process receives a request. To fulfill it, the process invokes the involved Web services and then responds to the original caller. Because the BPEL process communicates with other Web services, it relies heavily on the WSDL description of the Web services invoked by the composite Web service.
Question 8. What Are Two Configuration Settings For Auditing?
Answer :
auditLevel:
off - absolutely no logging performed whatsoever; may result in a slight performance boost for processing instances.
minimal - all events are logged; however, no audit details are logged.
production - all events are logged. The audit details for assign activities are not logged; the details for all other nodes are logged.
development - all events are logged; all audit details for all activities are logged.
auditDetailThreshold:
The maximum size (in bytes) an audit trail details string can be before it is stored separately from the audit trail. If a details string is larger than the threshold it will not be immediately loaded when the audit trail is initially retrieved; a link will be displayed with the size of the details string. Typically, the details string will contain the contents of a BPEL variable. In cases where the variable is very large performance may be severely impacted by logging it to the audit trail. The default value is 50 kilobytes.
Question 9. What Are Two Modes Of Invocation That Are Supported By Bpel Console?
Answer :
BPEL Console supports two modes of invocation: an HTML Form view and an XML Source mode.
The XML Source mode, shown below, allows you to enter XML source data directly into a text form and that source is passed, as is, to initiate the BPEL process. To simplify the use of this mode, you can configure default XML data in the deployment descriptor of the process, which will be pre-loaded into the XML data field .
Alternatively, the HTML Form view in the BPEL Console's Initiate tab will automatically generate an HTML input form (when possible), which can be used to provide the input values to initiate a BPEL process for testing purposes.
Question 10. What Are Alerts For Stuck Bpel Messages?
Answer :
An alert is displayed when there are stuck messages for asynchronous BPEL processes. A global time threshold is used identify stuck messages.
Alerts are displayed at multiple levels:
soa-infra
Composite
Flow Trace (PS4)
Question 11. Explain Bpelx:insertbefore Extension In An Assign Activity?
Answer :
The from-spec query within bpelx:insertBefore yields zero or more nodes. The node list is appended as child nodes to the target node specified by the to-spec query.
The to-spec query of the insertBefore operation points to one or more single L-Value nodes. If more than one node is returned, the first node is used as the reference node. The reference node must be an element node. The parent of the reference node must also be an element node. Otherwise, a bpel:selectionFailure fault is generated. The node list generated by the from-spec query selection is inserted before the reference node. The to-spec query cannot refer to a partner link.
The following example shows the syntax before the execution of . The value of addrVar is:
CA
94065
After the execution of the following syntax in the BPEL process file:
Redwood Shore>
The value of addrVar now becomes:
Redwood Shore
CA
94065
Question 12. What Are Two Types Of Events Supported By Bpel?
Answer :
Although fault handlers and scopes improve the robustness of BPEL processes considerably, you can also manage events.
BPEL supports two types of events:
Message events are triggered by incoming messages through operation invocation on port types.
Alarm events are time-related and are triggered either after a certain duration or at a specific time.
Question 13. How Many Tables Are Used For Mediator Instance Tracking?
Answer :
There are in total 5 tables which are used by mediator instance tracking:
Mediator_instance - One row for each mediator message flow.
Mediator_case_instance - One row for each mediator case (~ routing rule).
If a mediator component has two routing rules then this should have 2 records for that mediator instance.
Mediator_case_detail - Captures mediator audit trail for each mediator routing rule. Number of records may vary based on the nature of mediator component.
Eg: if mediator component is having a async req-resp routing rule then this would contain 2 rows for the corresponding mediator routing rule.
Mediator_document - Stores the payload for routing rules which are configured as deferred (~ parallel in jdev). So if all the routing rules are "sequential" then this will not contain any records.
Mediator_audit_document - Stores the payload for audit trail and only when "instanceTrackingLevel" for mediator is "Complete".
Question 14. What Are Various Sources Of Faults In Bpel?
Answer :
Business processes specified in BPEL will interact with partner processes through operation invocations on Web services. The communication between Web services is usually over internet connections that are not highly reliable. Web services can also raise faults due to logical and execution errors. Therefore, BPEL business processes need to handle faults appropriately and may also need to signal faults themselves.
Faults in BPEL can be from various sources:
A BPEL process can explicitly signal (throw) a fault.
A fault can occur when the BPEL process invokes a Web service operation. The operation might return a WSDL fault message, which results in a BPEL fault.
A fault can be thrown automatically by the BPEL runtime environment, either due to a certain condition in the BPEL process itself (such as a join failure), as a consequence of error conditions in the runtime environment, or related to network communication or other reasons. For such situations, BPEL defines several standard faults.
Question 15. How Can A Business Process Signal A Fault Explicitly?
Answer :
A business process sometimes needs to signal a fault explicitly. Therefore, BPEL provides the activity, which has the following syntax:
BPEL does not require definition of fault names prior to their use in the activity. This flexible approach can be error-prone, because there is no compile-time checking of fault names. In the case of typos, misspelled faults will not be handled by the designated fault handler.
Faults can also have an associated variable that contains fault data. If such a variable is required, you have to specify it when throwing a fault, by using the optional faultVariable
Question 16. How Can We Handle Faults In Bpel?
Answer :
When a fault occurs within a business process, the process may not complete successfully. (But it can complete successfully if the fault is handled within a scope, which enables you to divide a complex process into several parts; more on scopes later.) The business process can handle the fault through one or more fault handlers. Within a fault handler, the business process defines custom activities that should recover from the fault and possibly reverse the partial (unsuccessful) work of the activity where the fault has occurred.
The fault handlers are specified before the first activity of the BPEL process, after partner links and variables.
The overall structure is shown in the following code excerpt:
Within the fault handlers, you specify several activities where you indicate which fault you want to catch and handle. Within a fault handler, you must specify at least one or . The activity can be specified only once within a fault handler.
Usually you specify several activities where you will handle specific faults and use to handle all other faults. To specify which fault you would like to handle, you must specify at least one of the following:
faultName, which specifies the name of the fault to handle
faultVariable, which specifies the variable type used for fault data
The flexibility of activities is high, and all the following variations are permissible:
Fault handlers in BPEL are similar to try/catch clauses in modern programming languages such as Java.
Question 17. What Is Scopes In Bpel? How Can It Be Useful In Handling Faults?
Answer :
Scopes are hierarchically organized parts into which a complex business process can be divided. They provide behavioral contexts for activities. In other words, scopes enable you to define different fault handlers for different activities (or sets of activities gathered under a common structured activity such as or ). In addition to defining fault handlers, you can declare variables that are visible only within a scope. Scopes also let you define local correlation sets, compensation handlers, and event handlers.
Question 18. What Is Inline Fault Handling?
Answer :
In BPEL processes, invocation of operations on Web services can be particularly error-prone. There are numerous situations—such as broken connections, unavailability of Web services, or changes in the Web services WSDL—that can prevent a BPEL process from successfully invoking a partner Web service operation.
Such faults can be handled in the section of the corresponding scope.
Question 19. Explain The Use Of Message Event And Alarm Events?
Answer :
Managing message events is particularly important when the business process is waiting for callbacks from partner Web services. activity, lets you wait for only a single (exactly specified) message on a port type. Often, however, it is more useful to wait for more than one message, of which only one will occur.
Alarm events are useful when you want the process to wait for a callback for a certain period of time, such as 15 minutes. If no callback is received, the process flow continues as designed. This approach is particularly useful in loosely coupled service-oriented architectures, where you cannot rely on Web services being available all the time. This way, the process flow can proceed even if one of the bookstores does not return an offer.
Question 20. Explain Pick Activity Of Bpel?
Answer :
BPEL provides the activity, through which you can specify that the business process should await the occurrence of one event in a set of events. Events can be message events handled with the activity or alarm events handled with the activity. For each event, you specify an activity or a set of activities that should be performed.
Question 21. How Can We Use Pick As Initial Activity?
Answer :
You can use the activity instead of the initial activity. You can specify several operations, and receiving one of these messages will result in the creation of a business process instance. Then you have to use a special form of the activity. You specify the createInstance attribute for the activity, but you can specify only events; events are not permitted in this specific form.
To understand the use of this special form of the activity, consider the bookstore Web service, implemented as a simple BPEL process.
Question 22. How Xml Data Works In Bpel?
Answer :
In a BPEL process, every piece of data is in XML forms. This includes the messages passed to and from the BPEL process, the messages exchanged with external services, and local variables used by the process. You define the types for these messages and variables with the XML schema, usually in the WSDL file for the flow, the WSDL files for the services it invokes, or the XSD file referenced by those WSDL files. Therefore, all variables in BPEL are XML data, and any BPEL process uses much of its code to manipulate these XML variables. This typically includes performing data transformation between representations required for different services, and local manipulation of data (for example, to combine the results from several service invocations).
Question 23. What Is Use Of Assign Activity In Bpel?
Answer :
You use the assign activity to copy data from one XML variable to another, or to calculate the value of an expression and store it in a variable. A copy element within the activity specifies the source and target of the assignment (what to copy from and to), which must be of compatible types.
The formal syntax as shown in the Business Process Execution Language for Web Services Specification is as follows:
standard-elements
+
from-spec
to-spec
This syntax is described in detail in that specification. The from-spec and to-spec typically specify a variable or variable part, as in:
Example of assigning a numeric value to a variable in XPath expressions.
You can assign numeric values in XPath expressions. The following example shows how to assign an XPath expression with the integer value 100.
Question 24. How Can You Assign Boolean Values To A Field In Xpath Expression ?
Answer :
In this example of assigning Boolean values, the XPath expression in the from clause is a call to XPath's Boolean function true, and the specified approved field is set to true. The function false is also available.
The XPath specification recommends that you use the "true()" and "false()" functions as a method for returning Boolean constant values.
If you instead use "boolean(true)" or "boolean(false)", the true or false inside the Boolean function is interpreted as a relative element step, and not as any true or false constant. This means it attempts to select a child node named true under the current XPath context node. In most cases, the true node does not exist. Therefore, an empty result node set is returned and the boolean() function in XPath 1.0 converts an empty node set into a false result. This result can be potentially confusing.
Question 25. How Can You Assign The Current Value Of A Date Or Time Field By Using The Oracle Bpel Xpath Function Getcurrentdate, Getcurrenttime, Or Getcurrentdatetime ?
Answer :
You can assign the current value of a date or time field by using the Oracle BPEL XPath function getCurrentDate, getCurrentTime, or getCurrentDateTime, respectively. In addition, if you have a date-time value in the standard XSD format, you can convert it to characters more suitable for output by calling the Oracle BPEL XPath function formatDate.
In the next example, the formatDate function converts the date-time value provided in XSD format to the string 'Jun 10, 2005' (and assigns it to the string field formattedDate).
Question 26. Explain Bpelx:rename And Xsd Type Casting?
Answer :
The bpelx:rename extension in an assign activity enables a BPEL process to rename an element through use of XSD type casting.
The syntax of bpelx:target is similar to and a subset of to-spec for the copy operation. The target must return a list of one more element nodes. Otherwise, a bpel:selectionFailure fault is generated. The element nodes specified in the from-spec are renamed the QName specified by the elementTo attribute. The xsi:type attribute is added to those element nodes to cast those elements to the QName type specified by the typeCastTo attribute.
Assume you have the following employee list:
JohnDole
JaneDole
PeterSmith
MarySmith
Promotion changes are now applied to Peter Smith in the employee list:
After executing the above casting (renaming), the data looks as follows with xsi:type info added to Peter Smith:
JohnDole
JaneDole
3000
marysmith
The employee data of Peter Smith is now invalid, because and are missing. Therefore, is used to add that information.
2500
petersmith
2500
Question 27. Explain Bpelx:remove Extension In An Assign Activity?
Answer :
The bpelx: remove extension in an assign activity enables a BPEL process to remove a variable.
Node removal specified by the XPath expression is supported. Nodes specified by the XPath expression can be multiple, but must be L-Values. Nodes being removed from this parent can be text nodes, attribute nodes, and element nodes.
The XPath expression can return one or more nodes. If the XPath expression returns zero nodes, then a bpel:selectionFailure fault is generated.
The syntax of bpelx: target is similar to and a subset of to-spec for the copy operation.
The following example shows addrVar with the following value:
500 Oracle Parkway
Mailstop 1op6
CA
94065
After executing the following syntax in the BPEL process file, the second address line of Mailstop is removed.
Question 28. List Some Bpelx Extension Types To Perform Various Operations On Xml Data In Assign Activities?
Answer :
You may want to perform various operations on XML data in assign activities.
The following bpelx extension types provide this functionality:
bpelx:append
bpelx:insertBefore
bpelx:insertAfter
bpelx:remove
bpelx:rename and XSD Type Casting
bpelx:copyList
Question 29. What Are Two Audit Trial Tables Used In Bpel?
Answer :
There are 2 audit trail tables used in BPEL: audit_trail and audit_details.
All audit trail events are inserted into audit_trail. audit_details is used for the details section of an event (ie. payload); if a payload exceeds a certain size, it is inserted into audit_details instead of being inlined in the audit_trail event.
Question 30. Bpel Is Cross-platform, But Is There Any Advantage To Building The Underlying Services On A J2ee Platform? If So, What Are They?
Answer :
The J2EE platform is maturing towards better support for clustering, Virtualization and monitoring. By architecture the BPEL Process Manager as a set of J2EE components, we will transparently leverage those capabilities. Virtualization, automatic deployment, on-demand scalability, and self-healing are notions that marry very well with business processes so it will be very interesting to see those developments come together.
Question 31. How Important Is .net Compatibility? To What Extent Does Bpel Process Manager Support It?
Answer :
.NET is probably fourth or fifth on the list of systems customers want to integrate with, so it is fairly important. The BPEL Process Manager ships with examples showcasing how a BPEL process can invoke a .NET service as well as how a .NET client can initiate a BPEL process. We are looking at extending those samples to demonstrate security and reliable messaging.
Question 32. What Version Of The Bpel Standard Is Supported By Oracle Bpel Process Manager?
Answer :
BPEL PM 10.1.2 and 10.1.3 supports BPEL4WS 1.1. However, some features from WSBPEL 2.0 working draft have already been implemented in the BPEL PM 10.1.2 and 10.1.3 releases. We plan for full support for BPEL 2.0 shortly after it is released and expect a smooth migration path.
Question 33. Bpel Process Manager (as Well As Jdev, Adf, Toplink, Etc.) Run On Any J2ee Servers. Why Is Oracle So Committed To Open Standards And Open Interfaces?
Answer :
Because they are good for Oracle in that they allow us to leverage the hundreds of man-years invested in building a scalable and reliable container. And they are good for our customers in that they prevent them from being locked in.
Question 34. How Has/is Oracle Been Involved With The Evolution And Standardization Of The Bpel Spec? How Does This Relate To Oracle Other Integration And Web Service-related Standards Efforts?
Answer :
Oracle is a very active member of the OASIS BPEL committee. With more than 6,500 developers using the BPEL Process Manager, we are at the forefront of the adoption of BPEL and can circle back the feedback we are collecting to the committee. Oracle is also actively involved of peripheral specifications: WS-reliability, WS-message delivery, WS-context, WS-security, JSR-208/Java business integration. All these standards are coming together to transform the internet into a messaging/integration backbone. They will therefore play a very important role in the adoption of BPEL.
Question 35. How Will Oracle Business Integration Take Advantage Of Bpel And Bpel Process Manager Going Forward?
Answer :
SOA, BPEL, and composite applications bring us one step closer to "real-time enterprise." We believe that rich business activity monitoring is the next step as it provides details visibility into the execution of cross-functional processes and a platform of business process optimization. You should expect to see a lot more from Oracle on that aspect of the solution going forward.
Question 36. Why Is Native Bpel Important? What Is The Disadvantage Of Products That Only Import/export Bpel?
Answer :
Historically every time a standard has been adopted (SQL, J2EE, LDAP, SMTP/POP/IMAP, HTML, etc.), native solutions have won. It is because native solutions are less complex, faster and offer richer functionality. It is also because re-architecting an engine around a new abstraction is very difficult, especially if you have an existing install base that you need to maintain and evolve in parallel.
Question 37. What Exactly Is Oracle Bpel Process Manager? What Is It Composed Of? How Does It Relate To The Rest Of The Stack?
Answer :
The Oracle BPEL Process Manager is a new addition to the Oracle product portfolio. It enables enterprises to model, deploy and manage BPEL processes. It comprises an easy-to-use BPEL modeler, a scalable BPEL engine, an extensible WSDL binding framework, a monitoring console and a set of built-in integration services (transformation, user task, java embedding). It makes BPEL/Web service orchestration a first class citizen of the Java platform.
Question 38. What Is Orchestration? What Does It Mean To Build Composite Applications? Why Would Anyone Want To?
Answer :
Existing systems are not going away. Yet enterprises need to build new applications that can leverage the functionality encapsulated in those existing systems. The notion of a composite application is based around the idea of building new applications by wiring together existing building blocks. Orchestration plays an important role in this picture because it is the glue that coordinates the execution of each discrete service. A good orchestration server needs to be reliable, scalable and render the BPEL process logic with very high fidelity.
Question 39. What Is/was The Motivation Behind Bpel? How Does It Differ From Other/past Attempts/technologies Aimed At The Integration/business Process Problem? Can You Talk Briefly About The Evolution Of Bpel?
Answer :
Orchestrating a set of services into an end-to-end process flow entails a new set of technical requirements (binding to heterogeneous system, synchronous and asynchronous message exchange patterns, data manipulation, flow coordination, exception management, undeterministic events, compensating transactions, side-by-side versioning, in-flight instance management and auditing). The goal of BPEL is provide a richer and yet simpler abstraction/standard for addressing those requirements. Although it is a fairly new standard, it leverages from 10+ years of research and development Microsoft and IBM invested in XLANG and WSFL.
Question 40. What Is Bpel? How Does It Relate To Web Services And Service-oriented Architecture (soa)?
Answer :
There is a constant pressure for businesses to interconnect their applications. This is what is driving the adoption of web services and SOA as an enterprise blue print for reducing the cost and complexity of integration initiatives. Making web services work is a two-step process: first you publish and then you orchestrate. Publish means taking a part of a existing system and exposing it as a service. Orchestrate means composing multiple discrete services into an end-to-end process flow. BPEL is the industry standard for orchestration.
Question 41. What Is Bpel Process In Soa ?
Answer :
(Business Process Execution Language) BPEL Process is a language used for the composition, orchestration and coordination of webservics. In this post we will explain BPEL, define the BPEL role with regard to Service Oriented Architecture and explain the process-oriented approach to SOA and the role of BPEL.
In BPEL the Enterprise application and information systems have become more more fundamental assets to companies. The Companies are trust on them to be able to perform business operations.
Enterprise Information system can improve the efficiency of businesses through the automation of business processes. The objective of almost every company is that the application it uses should provide comprehensive support for business processes. It means that applications should align with business processes closely.
BPEL Role of business processes and their challenges,BPEL Business and IT alignment,What are BPEL features,what are BPEL features, BPEL Orchestration and Choreography, Examine the relation of BPEL to other Languages, The future of BPEL.
Already existing applications have often been developed using older technologies, languages and architectures, which are by definition less flexible to change. Such C,C++, and Mainframe. These applications are tightly coupled applications, constructed of interrelated modules, these are can not be differentiated, upgraded, or refactored with reasonable amount of effort, place important limitations on the flexibility of such applications.
Already existing applications are also difficult to modify and adapt because they have not been developed in a flexible way that would allow modifying application parts quickly and efficiently. Modifying existing applications are require more time Complexity of existing applications and the overall IT Architecture, Modifying them is a complex, difficult and time-consuming task.
Question 42. What Are Predefined Errors In Bpel?
Answer :
Custom errors
Timed out errors
BPM errors
Validation Errors
Question 43. How Can You Increase Performance In Bpel?
Answer :
We can increase the performance by writing indexes and sequences. (Or) Go to application server - Configurations - Change Xml file
Question 1. What Is Soa ?
Answer :
SOA stands for Service Oriented Architecture. SOA is not any tool, rather is a concept and there are many tools in the market based upon this concept. In this SOA Concept, we use SOA layer as middle or intermediate layer between services so that these service can communicate with each other.
Question 2. Benefits Of Soa ?
Answer :
Below are the major benefits that we get from SOA.
Loose Coupling : This means that the service requester has no knowledge of the technical details of the provider’s implementation, such as the programming language, deployment platform, and so forth. The service requester typically invokes operations by way of messages — a request message and the response — rather than through the use of APIs or file formats.
Cost Cutting
Better reuse: Build new client functionality on top of existing Business Services.
Well defined interfaces: Make changes without affecting clients
Easier to maintain : Changes/Versions are not all-or-nothing
Better flexibility
Question 3. What Is Oracle Soa Suite Tool ?
Answer :
SOA Suite tool is a middleware tool from Oracle which is based upon SOA concept comes under Oracle Fusion Middleware stack. We use this tool for integration purpose .i.e. This tool is used to integrate two system/applications etc.
Question 4. Is Oracle Soa Suite Tool State Full ?
Answer :
Yes SOA Suite tool is a state full tool, that means in this tool we store every state in database i.e. we store all the incoming messages, transformed messages, outgoing messages to database along with timestamp.
Question 5. How Many Components We Have In Oracle Soa Suite Tool?
Answer :
We have total 5 components in Oracle SOA Suite tool as mentioned below.
BPEL : Business Process Execution Language
Mediator
Business Rules
Human Task
Spring
Question 6. What All Components/products Needs To Be Installed Before We Install Oracle Soa Suite Tool ?
Answer :
Following components needs to be installed before we install Oracle SOA Suite.
JDK
Database
All Required Schema (Created using RCU)
WebLogic Server
Question 7. Which Application Server Required For Oracle Soa Suite Tool ?
Answer :
Mostly WebLogic server is used as application server for Oracle SOA Suite tool.
Question 8. Which Ide We Use For Oracle Soa Suite Tool ?
Answer :
We use JDeveloper IDE for Oracle SOA suite tool.
Question 9. What Is Domain ?
Answer :
A domain is the basic administration unit for WebLogic Server instances. i.e. Domains include a special WebLogic Server instance called the Administration Server, which is the central point from which you configure and manage all resources in the domain.
Question 10. What Is Administration Server ?
Answer :
A domain has one WLS instance configured as an admin server. The admin server provides a central point for managing a domain.
Question 11. What Is Managed Servers ?
Answer :
All other WLS instances in a domain are called Managed Servers. Managed servers host application components and resources.
Question 12. What Is Cluster ?
Answer :
Cluster is a group of server instances that work together as a single runtime unit from a client perspective. Clustering provides scalability and high availability for applications.
Question 13. What Is Em ?
Answer :
EM stands for Enterprise Manager. It is webpage we deploy, test, monitor, diagnose and resolve problem for composites. It is hosted on the Admin Server.
Question 14. What Is Soa-infra ?
Answer :
soa-infra is a J2EE application that is targeted to either a managed server or a cluster. All the composites gets deployed under soa-infra application.
Question 15. What All Schema We Need For Oracle Soa Suite Tool ?
Answer :
We require following schema.
MDS – This schema is used to store all the artifacts like WSDL, XML, XSD etc.
SOA_INFRA – This schema is used to store SOA Component Engine properties, deployed composites, payloads, runtime metadata etc.
ORABAM – This schema is used to store the metadata that is related to BAM and its components and this is optional schema.
ORASDPM – This schema is used to store metadata about the user messaging systems.
Question 16. What Is Partition ?
Answer :
Sections of the SOA Infrastructure where we deploy SOA composite applications known as partition. When we install SOA suite tool, default partition get created with name “default” but we can add as many as partitions as required.
Question 17. What Are Benefits Of Partition?
Answer :
Below are the major benefits of partition.
Logically group SOA composites.
Perform bulk lifecycle management tasks on large numbers of composites.
Question 18. What All Bulk Operations We Can Perform On Partition ?
Answer :
We can perform below operations.
Start all composites
Shut down all composites
Undeploy all composites
Retire all composites
Activate all composites
List all composites
Question 19. How We Can Deploy Composite To Soa Server ?
Answer :
There are different methods to deploy SOA composite to SOA server.
Through EM console
Directly from JDeveloper
Scripting (Ant, WLST etc.)
Question 20. What Is Config Plan ?
Answer :
Config plan is used during composite deployment. This is a xml file where we specify the parameters that we want to replace while doing the deployment to next environment.
Question 21. Can We Have Multiple Composites With Same Name On Soa Server ?
Answer :
Yes, we can have multiple composites with same name on SOA server but this is possible when we have composites with revisions.
Question 22. If We Have Multiple Composites On Soa Server With Same Name Then How Composites Run ?
Answer :
If we have multiple composites with same name then only one composite will act as default composite which will run only. But we can go to EM console and make other composite default.
Question 23. What Role Does Zookeeper Plays In Hbase?
Answer :
HBase comes integrated with Zoo keeper. When I start HBase, Zoo keeper instance is also started. The reason is that the Zoo keeper helps us in keeping a track of all region servers that are there for HBase. Zoo keeper keeps track of how many region servers are there, which region servers are holding from which data node to which data node. It keeps track of smaller data sets where Hadoop is missing out. It decreases the overhead on top of Hadoop which keeps track of most of your Meta data. Hence HMaster gets the details of region servers by actually contacting Zoo keeper.
Question 24. What Is Memstore ?
Answer :
The MemStore is a write buffer where HBase accumulates data in memory before a permanent write.
Its contents are flushed to disk to form an HFile when the MemStore fills up.It doesn’t write to an existing HFile but instead forms a new file on every flush. There is one MemStore per column family.
Question 25. What Is Wal ?
Answer :
We cannot be sure that the data will be persistent throughout in Memstore. Assume that a particular datanode is down. Then the data that resides on that data node’s memory will be lost.
To overcome this problem, when the request comes from the master it written to WAL as well. WAL is nothing but Write Ahead Logs which resides on the HDFS, a permanent storage. Now we can make sure that even when if the data node is down the data will not be lost I.e. we have the copy of all the actions that you are supposed to do in the WAL.
Question 26. What Are The Two Types Of Table Design Approach In Hbase?
Answer :
They are − (i) Short and Wide (ii) Tall and Thin
Question 27. Benefits Of Sca ?
Answer :
Easier Development :No need to write lengthy code as we get all components prebuilt.
Easily compose a assembly (composite) by just linking different these prebuilt components.
Better re-usability
Question 28. What Is Soa Composite ?
Answer :
SOA composite is a assembly comprises of one or more than one pre-build components. In SOA composite we wires different components together to perform required business functionality.
Question 29. What Is Service Component ?
Answer :
All prebuilt components BPEL , Mediator, Business Rules, Human Task and Spring known as service components.
Question 30. Can We Have More Than One Service Component In One Composite ?
Answer :
yes, we can have as many as service components in one composite but it is not recommended, we should not have all the components in one composite itself.
Question 31. How These Service Components Works ?
Answer :
Each service component is hosted in its own service engine container. E.g. Any logic added in BPEL components will be handled by BPEL service engine only.
Question 32. What Is Binding Component ?
Answer :
As name suggest, this component is used to bind composite application to external world. i.e. we use these components to link composite with source and target system.
Question 33. What Are The Types Of Binding Components ?
Answer :
Binding components are of two types as mentioned below.
Service Binding : With the help of this binding we connect composite to source or client system or we can say this is entry point of composite.
Reference Binding: This binding helps composite to connect to target or reference systems or we can say it is exist point of the composite.
Question 34. Can We More Than One Service & Reference Binding In One Composite ?
Answer :
Yes, we can more than one service & reference binding in one composite, that means we can have more than one entry & exist point for composite.
Question 35. What Can Be Scenario Where We Have Two Service Binding In One Composite ?
Answer :
When a composite can be initiated either by direct call or by consuming the same message from JMS queue, in this scenario we have two entry point for same composite.
Question 36. What Can Scenario Where We Have Two Reference Binding In One Composite ?
Answer :
Composite needs to send the message to first target by JMS queue and to other target by writing the file, in this scenario we have two exist for composite.
Question 37. What Is Wire ?
Answer :
Connection between service & binding component and within service & binding components know as wire. I.e. This enable us to graphically connect the components in a SOA composite application.
Question 38. What Is Bpel ?
Answer :
BPEL stands for Business Process Execution Language, it is one of the component of SOA Suite tool. BPEL is a XML based language used to design business process/flows. We perform service orchestration in BPEL.
Question 39. What Are Different Parts Of Bpel ?
Answer :
Below are different parts of BPEL as mentioned below.
Service Interface: A WSDL describing the functionality of the BPEL process. The service interface provides the end user a way to interact with the BPEL process component using Service Interface / Service Binding.
Activities: units of work. The actual elements that make up the BPEL process flow or sequence of instructions to be executed.
Partner links: also called Reference bindings. A partner link describes the roles played for the interaction between the BPEL process and the service it invokes.
Question 40. What All Bpel Templates Are Available In Soa Suite Tool ?
Answer :
Primarily we have three types of BPEL template in SOA Suite tool.
Synchronous BPEL Template
Asynchronous BPEL Template
OneWay BPEL Template
Answer :
Within the enterprise, BPEL is used to standardize enterprise application integration as well as to extend the integration to previously isolated systems. Between enterprises, BPEL enables easier and more effective integration with business partners. BPEL stimulates enterprises to further define their business processes, which in turn leads to business process optimization, reengineering, and the selection of the most appropriate processes, thus further optimizing the organization.
Definitions of business processes described in BPEL do not affect existing systems, thereby stimulating upgrades. BPEL is the key technology in environments where functionalities are already or will be exposed via Web services. With increases in the use of Web services, the importance of BPEL will increase as well.
BPEL represents a convergence of two early workflow languages; Web Services Flow Language (WSFL) and XLANG. WSFL was designed by IBM and is based on the concept of directed graphs. XLANG, a block-structured language, was designed by Microsoft. BPEL combines both approaches and provides a rich vocabulary for description of business processes.
Question 2. What Is Oracle Jdeveloper?
Answer :
Oracle BPEL Process Manager provides support for using Oracle JDeveloper to graphically design BPEL processes.
Oracle JDeveloper is an integrated development environment (IDE) for building applications and Web services using Java, XML, and SQL standards. Oracle JDeveloper supports the entire development life cycle with integrated features for designing, coding, debugging, testing, profiling, tuning, and deploying applications. A visual and declarative development approach and the Oracle Application Development Framework (ADF) work together to simplify application development and reduce coding tasks.
Oracle JDeveloper uses BPEL as its native format. This means that processes built with Oracle JDeveloper are 100% portable. Oracle JDeveloper also enables you to view and modify the BPEL source without decreasing the usefulness of the tool.
You design BPEL processes by dragging and dropping elements (known as activities) into the process and editing their property pages. This eliminates the need to write BPEL code. You integrate BPEL processes with external services (known as partner links). You also integrate adapters and services such as workflows, transformations, notifications, sensors, worklist task management, and business rules with the process. Oracle JDeveloper can deploy the developed processes directly to Oracle BPEL Server. This facilitates the development and maintenance of BPEL processes.
Oracle BPEL Process Manager provides support for the following services and adapters in Oracle JDeveloper:
Transformations, workflows, worklists, notifications, sensors, and business rules
Technology adapters (file, FTP, database, AQ, JMS, MQ, and Oracle Applications)
Question 3. What Are Two Ways Of Combining Web Services?
Answer :
Web services can be combined in two ways:
Orchestration
Choreography
Question 4. Explain Orchestration And Choreography?
Answer :
In orchestration, which is usually used in private business processes, a central process (which can be another Web service) takes control of the involved Web services and coordinates the execution of different operations on the Web services involved in the operation. The involved Web services do not "know" (and do not need to know) that they are involved in a composition process and that they are taking part in a higher-level business process. Only the central coordinator of the orchestration is aware of this goal, so the orchestration is centralized with explicit definitions of operations and the order of invocation of Web services.
Choreography, in contrast, does not rely on a central coordinator. Rather, each Web service involved in the choreography knows exactly when to execute its operations and with whom to interact. Choreography is a collaborative effort focusing on the exchange of messages in public business processes. All participants in the choreography need to be aware of the business process, operations to execute, messages to exchange, and the timing of message exchanges.
Question 5. What Are Two Different Ways Of Describing Business Processes That Are Supported By Bpel?
Answer :
BPEL supports two different ways of describing business processes that support orchestration and choreography:
Executable processes allow you to specify the exact details of business processes. They follow the orchestration paradigm and can be executed by an orchestration engine.
Abstract business protocols allow specification of the public message exchange between parties only. They do not include the internal details of process flows and are not executable. They follow the choreography paradigm.
Question 6. List Of All Primitive Activities Supported By Bpel Business Process?
Answer :
Primitive activities represent basic constructs and are used for common tasks, such as the following:
Invoking other Web services.
Waiting for the client to invoke the business process by sending a message.
Generating a response for synchronous operations.
Manipulating data variables.
Indicating faults and exceptions.
Waiting for some time.
Terminating the entire process.
Question 7. What Is The Use Of Bpel Business Process?
Answer :
In a typical scenario, the BPEL business process receives a request. To fulfill it, the process invokes the involved Web services and then responds to the original caller. Because the BPEL process communicates with other Web services, it relies heavily on the WSDL description of the Web services invoked by the composite Web service.
Question 8. What Are Two Configuration Settings For Auditing?
Answer :
auditLevel:
off - absolutely no logging performed whatsoever; may result in a slight performance boost for processing instances.
minimal - all events are logged; however, no audit details are logged.
production - all events are logged. The audit details for assign activities are not logged; the details for all other nodes are logged.
development - all events are logged; all audit details for all activities are logged.
auditDetailThreshold:
The maximum size (in bytes) an audit trail details string can be before it is stored separately from the audit trail. If a details string is larger than the threshold it will not be immediately loaded when the audit trail is initially retrieved; a link will be displayed with the size of the details string. Typically, the details string will contain the contents of a BPEL variable. In cases where the variable is very large performance may be severely impacted by logging it to the audit trail. The default value is 50 kilobytes.
Question 9. What Are Two Modes Of Invocation That Are Supported By Bpel Console?
Answer :
BPEL Console supports two modes of invocation: an HTML Form view and an XML Source mode.
The XML Source mode, shown below, allows you to enter XML source data directly into a text form and that source is passed, as is, to initiate the BPEL process. To simplify the use of this mode, you can configure default XML data in the deployment descriptor of the process, which will be pre-loaded into the XML data field .
Alternatively, the HTML Form view in the BPEL Console's Initiate tab will automatically generate an HTML input form (when possible), which can be used to provide the input values to initiate a BPEL process for testing purposes.
Question 10. What Are Alerts For Stuck Bpel Messages?
Answer :
An alert is displayed when there are stuck messages for asynchronous BPEL processes. A global time threshold is used identify stuck messages.
Alerts are displayed at multiple levels:
soa-infra
Composite
Flow Trace (PS4)
Question 11. Explain Bpelx:insertbefore Extension In An Assign Activity?
Answer :
The from-spec query within bpelx:insertBefore yields zero or more nodes. The node list is appended as child nodes to the target node specified by the to-spec query.
The to-spec query of the insertBefore operation points to one or more single L-Value nodes. If more than one node is returned, the first node is used as the reference node. The reference node must be an element node. The parent of the reference node must also be an element node. Otherwise, a bpel:selectionFailure fault is generated. The node list generated by the from-spec query selection is inserted before the reference node. The to-spec query cannot refer to a partner link.
The following example shows the syntax before the execution of . The value of addrVar is:
CA
94065
After the execution of the following syntax in the BPEL process file:
Redwood Shore>
The value of addrVar now becomes:
Redwood Shore
CA
94065
Question 12. What Are Two Types Of Events Supported By Bpel?
Answer :
Although fault handlers and scopes improve the robustness of BPEL processes considerably, you can also manage events.
BPEL supports two types of events:
Message events are triggered by incoming messages through operation invocation on port types.
Alarm events are time-related and are triggered either after a certain duration or at a specific time.
Question 13. How Many Tables Are Used For Mediator Instance Tracking?
Answer :
There are in total 5 tables which are used by mediator instance tracking:
Mediator_instance - One row for each mediator message flow.
Mediator_case_instance - One row for each mediator case (~ routing rule).
If a mediator component has two routing rules then this should have 2 records for that mediator instance.
Mediator_case_detail - Captures mediator audit trail for each mediator routing rule. Number of records may vary based on the nature of mediator component.
Eg: if mediator component is having a async req-resp routing rule then this would contain 2 rows for the corresponding mediator routing rule.
Mediator_document - Stores the payload for routing rules which are configured as deferred (~ parallel in jdev). So if all the routing rules are "sequential" then this will not contain any records.
Mediator_audit_document - Stores the payload for audit trail and only when "instanceTrackingLevel" for mediator is "Complete".
Question 14. What Are Various Sources Of Faults In Bpel?
Answer :
Business processes specified in BPEL will interact with partner processes through operation invocations on Web services. The communication between Web services is usually over internet connections that are not highly reliable. Web services can also raise faults due to logical and execution errors. Therefore, BPEL business processes need to handle faults appropriately and may also need to signal faults themselves.
Faults in BPEL can be from various sources:
A BPEL process can explicitly signal (throw) a fault.
A fault can occur when the BPEL process invokes a Web service operation. The operation might return a WSDL fault message, which results in a BPEL fault.
A fault can be thrown automatically by the BPEL runtime environment, either due to a certain condition in the BPEL process itself (such as a join failure), as a consequence of error conditions in the runtime environment, or related to network communication or other reasons. For such situations, BPEL defines several standard faults.
Question 15. How Can A Business Process Signal A Fault Explicitly?
Answer :
A business process sometimes needs to signal a fault explicitly. Therefore, BPEL provides the activity, which has the following syntax:
BPEL does not require definition of fault names prior to their use in the activity. This flexible approach can be error-prone, because there is no compile-time checking of fault names. In the case of typos, misspelled faults will not be handled by the designated fault handler.
Faults can also have an associated variable that contains fault data. If such a variable is required, you have to specify it when throwing a fault, by using the optional faultVariable
Question 16. How Can We Handle Faults In Bpel?
Answer :
When a fault occurs within a business process, the process may not complete successfully. (But it can complete successfully if the fault is handled within a scope, which enables you to divide a complex process into several parts; more on scopes later.) The business process can handle the fault through one or more fault handlers. Within a fault handler, the business process defines custom activities that should recover from the fault and possibly reverse the partial (unsuccessful) work of the activity where the fault has occurred.
The fault handlers are specified before the first activity of the BPEL process, after partner links and variables.
The overall structure is shown in the following code excerpt:
Within the fault handlers, you specify several activities where you indicate which fault you want to catch and handle. Within a fault handler, you must specify at least one or . The activity can be specified only once within a fault handler.
Usually you specify several activities where you will handle specific faults and use to handle all other faults. To specify which fault you would like to handle, you must specify at least one of the following:
faultName, which specifies the name of the fault to handle
faultVariable, which specifies the variable type used for fault data
The flexibility of activities is high, and all the following variations are permissible:
Fault handlers in BPEL are similar to try/catch clauses in modern programming languages such as Java.
Question 17. What Is Scopes In Bpel? How Can It Be Useful In Handling Faults?
Answer :
Scopes are hierarchically organized parts into which a complex business process can be divided. They provide behavioral contexts for activities. In other words, scopes enable you to define different fault handlers for different activities (or sets of activities gathered under a common structured activity such as or ). In addition to defining fault handlers, you can declare variables that are visible only within a scope. Scopes also let you define local correlation sets, compensation handlers, and event handlers.
Question 18. What Is Inline Fault Handling?
Answer :
In BPEL processes, invocation of operations on Web services can be particularly error-prone. There are numerous situations—such as broken connections, unavailability of Web services, or changes in the Web services WSDL—that can prevent a BPEL process from successfully invoking a partner Web service operation.
Such faults can be handled in the section of the corresponding scope.
Question 19. Explain The Use Of Message Event And Alarm Events?
Answer :
Managing message events is particularly important when the business process is waiting for callbacks from partner Web services. activity, lets you wait for only a single (exactly specified) message on a port type. Often, however, it is more useful to wait for more than one message, of which only one will occur.
Alarm events are useful when you want the process to wait for a callback for a certain period of time, such as 15 minutes. If no callback is received, the process flow continues as designed. This approach is particularly useful in loosely coupled service-oriented architectures, where you cannot rely on Web services being available all the time. This way, the process flow can proceed even if one of the bookstores does not return an offer.
Question 20. Explain Pick Activity Of Bpel?
Answer :
BPEL provides the activity, through which you can specify that the business process should await the occurrence of one event in a set of events. Events can be message events handled with the activity or alarm events handled with the activity. For each event, you specify an activity or a set of activities that should be performed.
Question 21. How Can We Use Pick As Initial Activity?
Answer :
You can use the activity instead of the initial activity. You can specify several operations, and receiving one of these messages will result in the creation of a business process instance. Then you have to use a special form of the activity. You specify the createInstance attribute for the activity, but you can specify only events; events are not permitted in this specific form.
To understand the use of this special form of the activity, consider the bookstore Web service, implemented as a simple BPEL process.
Question 22. How Xml Data Works In Bpel?
Answer :
In a BPEL process, every piece of data is in XML forms. This includes the messages passed to and from the BPEL process, the messages exchanged with external services, and local variables used by the process. You define the types for these messages and variables with the XML schema, usually in the WSDL file for the flow, the WSDL files for the services it invokes, or the XSD file referenced by those WSDL files. Therefore, all variables in BPEL are XML data, and any BPEL process uses much of its code to manipulate these XML variables. This typically includes performing data transformation between representations required for different services, and local manipulation of data (for example, to combine the results from several service invocations).
Question 23. What Is Use Of Assign Activity In Bpel?
Answer :
You use the assign activity to copy data from one XML variable to another, or to calculate the value of an expression and store it in a variable. A copy element within the activity specifies the source and target of the assignment (what to copy from and to), which must be of compatible types.
The formal syntax as shown in the Business Process Execution Language for Web Services Specification is as follows:
standard-elements
+
from-spec
to-spec
This syntax is described in detail in that specification. The from-spec and to-spec typically specify a variable or variable part, as in:
Example of assigning a numeric value to a variable in XPath expressions.
You can assign numeric values in XPath expressions. The following example shows how to assign an XPath expression with the integer value 100.
Question 24. How Can You Assign Boolean Values To A Field In Xpath Expression ?
Answer :
In this example of assigning Boolean values, the XPath expression in the from clause is a call to XPath's Boolean function true, and the specified approved field is set to true. The function false is also available.
The XPath specification recommends that you use the "true()" and "false()" functions as a method for returning Boolean constant values.
If you instead use "boolean(true)" or "boolean(false)", the true or false inside the Boolean function is interpreted as a relative element step, and not as any true or false constant. This means it attempts to select a child node named true under the current XPath context node. In most cases, the true node does not exist. Therefore, an empty result node set is returned and the boolean() function in XPath 1.0 converts an empty node set into a false result. This result can be potentially confusing.
Question 25. How Can You Assign The Current Value Of A Date Or Time Field By Using The Oracle Bpel Xpath Function Getcurrentdate, Getcurrenttime, Or Getcurrentdatetime ?
Answer :
You can assign the current value of a date or time field by using the Oracle BPEL XPath function getCurrentDate, getCurrentTime, or getCurrentDateTime, respectively. In addition, if you have a date-time value in the standard XSD format, you can convert it to characters more suitable for output by calling the Oracle BPEL XPath function formatDate.
In the next example, the formatDate function converts the date-time value provided in XSD format to the string 'Jun 10, 2005' (and assigns it to the string field formattedDate).
Question 26. Explain Bpelx:rename And Xsd Type Casting?
Answer :
The bpelx:rename extension in an assign activity enables a BPEL process to rename an element through use of XSD type casting.
The syntax of bpelx:target is similar to and a subset of to-spec for the copy operation. The target must return a list of one more element nodes. Otherwise, a bpel:selectionFailure fault is generated. The element nodes specified in the from-spec are renamed the QName specified by the elementTo attribute. The xsi:type attribute is added to those element nodes to cast those elements to the QName type specified by the typeCastTo attribute.
Assume you have the following employee list:
JohnDole
JaneDole
PeterSmith
MarySmith
Promotion changes are now applied to Peter Smith in the employee list:
After executing the above casting (renaming), the data looks as follows with xsi:type info added to Peter Smith:
JohnDole
JaneDole
3000
marysmith
The employee data of Peter Smith is now invalid, because and are missing. Therefore, is used to add that information.
2500
petersmith
2500
Question 27. Explain Bpelx:remove Extension In An Assign Activity?
Answer :
The bpelx: remove extension in an assign activity enables a BPEL process to remove a variable.
Node removal specified by the XPath expression is supported. Nodes specified by the XPath expression can be multiple, but must be L-Values. Nodes being removed from this parent can be text nodes, attribute nodes, and element nodes.
The XPath expression can return one or more nodes. If the XPath expression returns zero nodes, then a bpel:selectionFailure fault is generated.
The syntax of bpelx: target is similar to and a subset of to-spec for the copy operation.
The following example shows addrVar with the following value:
500 Oracle Parkway
Mailstop 1op6
CA
94065
After executing the following syntax in the BPEL process file, the second address line of Mailstop is removed.
Question 28. List Some Bpelx Extension Types To Perform Various Operations On Xml Data In Assign Activities?
Answer :
You may want to perform various operations on XML data in assign activities.
The following bpelx extension types provide this functionality:
bpelx:append
bpelx:insertBefore
bpelx:insertAfter
bpelx:remove
bpelx:rename and XSD Type Casting
bpelx:copyList
Question 29. What Are Two Audit Trial Tables Used In Bpel?
Answer :
There are 2 audit trail tables used in BPEL: audit_trail and audit_details.
All audit trail events are inserted into audit_trail. audit_details is used for the details section of an event (ie. payload); if a payload exceeds a certain size, it is inserted into audit_details instead of being inlined in the audit_trail event.
Question 30. Bpel Is Cross-platform, But Is There Any Advantage To Building The Underlying Services On A J2ee Platform? If So, What Are They?
Answer :
The J2EE platform is maturing towards better support for clustering, Virtualization and monitoring. By architecture the BPEL Process Manager as a set of J2EE components, we will transparently leverage those capabilities. Virtualization, automatic deployment, on-demand scalability, and self-healing are notions that marry very well with business processes so it will be very interesting to see those developments come together.
Question 31. How Important Is .net Compatibility? To What Extent Does Bpel Process Manager Support It?
Answer :
.NET is probably fourth or fifth on the list of systems customers want to integrate with, so it is fairly important. The BPEL Process Manager ships with examples showcasing how a BPEL process can invoke a .NET service as well as how a .NET client can initiate a BPEL process. We are looking at extending those samples to demonstrate security and reliable messaging.
Question 32. What Version Of The Bpel Standard Is Supported By Oracle Bpel Process Manager?
Answer :
BPEL PM 10.1.2 and 10.1.3 supports BPEL4WS 1.1. However, some features from WSBPEL 2.0 working draft have already been implemented in the BPEL PM 10.1.2 and 10.1.3 releases. We plan for full support for BPEL 2.0 shortly after it is released and expect a smooth migration path.
Question 33. Bpel Process Manager (as Well As Jdev, Adf, Toplink, Etc.) Run On Any J2ee Servers. Why Is Oracle So Committed To Open Standards And Open Interfaces?
Answer :
Because they are good for Oracle in that they allow us to leverage the hundreds of man-years invested in building a scalable and reliable container. And they are good for our customers in that they prevent them from being locked in.
Question 34. How Has/is Oracle Been Involved With The Evolution And Standardization Of The Bpel Spec? How Does This Relate To Oracle Other Integration And Web Service-related Standards Efforts?
Answer :
Oracle is a very active member of the OASIS BPEL committee. With more than 6,500 developers using the BPEL Process Manager, we are at the forefront of the adoption of BPEL and can circle back the feedback we are collecting to the committee. Oracle is also actively involved of peripheral specifications: WS-reliability, WS-message delivery, WS-context, WS-security, JSR-208/Java business integration. All these standards are coming together to transform the internet into a messaging/integration backbone. They will therefore play a very important role in the adoption of BPEL.
Question 35. How Will Oracle Business Integration Take Advantage Of Bpel And Bpel Process Manager Going Forward?
Answer :
SOA, BPEL, and composite applications bring us one step closer to "real-time enterprise." We believe that rich business activity monitoring is the next step as it provides details visibility into the execution of cross-functional processes and a platform of business process optimization. You should expect to see a lot more from Oracle on that aspect of the solution going forward.
Question 36. Why Is Native Bpel Important? What Is The Disadvantage Of Products That Only Import/export Bpel?
Answer :
Historically every time a standard has been adopted (SQL, J2EE, LDAP, SMTP/POP/IMAP, HTML, etc.), native solutions have won. It is because native solutions are less complex, faster and offer richer functionality. It is also because re-architecting an engine around a new abstraction is very difficult, especially if you have an existing install base that you need to maintain and evolve in parallel.
Question 37. What Exactly Is Oracle Bpel Process Manager? What Is It Composed Of? How Does It Relate To The Rest Of The Stack?
Answer :
The Oracle BPEL Process Manager is a new addition to the Oracle product portfolio. It enables enterprises to model, deploy and manage BPEL processes. It comprises an easy-to-use BPEL modeler, a scalable BPEL engine, an extensible WSDL binding framework, a monitoring console and a set of built-in integration services (transformation, user task, java embedding). It makes BPEL/Web service orchestration a first class citizen of the Java platform.
Question 38. What Is Orchestration? What Does It Mean To Build Composite Applications? Why Would Anyone Want To?
Answer :
Existing systems are not going away. Yet enterprises need to build new applications that can leverage the functionality encapsulated in those existing systems. The notion of a composite application is based around the idea of building new applications by wiring together existing building blocks. Orchestration plays an important role in this picture because it is the glue that coordinates the execution of each discrete service. A good orchestration server needs to be reliable, scalable and render the BPEL process logic with very high fidelity.
Question 39. What Is/was The Motivation Behind Bpel? How Does It Differ From Other/past Attempts/technologies Aimed At The Integration/business Process Problem? Can You Talk Briefly About The Evolution Of Bpel?
Answer :
Orchestrating a set of services into an end-to-end process flow entails a new set of technical requirements (binding to heterogeneous system, synchronous and asynchronous message exchange patterns, data manipulation, flow coordination, exception management, undeterministic events, compensating transactions, side-by-side versioning, in-flight instance management and auditing). The goal of BPEL is provide a richer and yet simpler abstraction/standard for addressing those requirements. Although it is a fairly new standard, it leverages from 10+ years of research and development Microsoft and IBM invested in XLANG and WSFL.
Question 40. What Is Bpel? How Does It Relate To Web Services And Service-oriented Architecture (soa)?
Answer :
There is a constant pressure for businesses to interconnect their applications. This is what is driving the adoption of web services and SOA as an enterprise blue print for reducing the cost and complexity of integration initiatives. Making web services work is a two-step process: first you publish and then you orchestrate. Publish means taking a part of a existing system and exposing it as a service. Orchestrate means composing multiple discrete services into an end-to-end process flow. BPEL is the industry standard for orchestration.
Question 41. What Is Bpel Process In Soa ?
Answer :
(Business Process Execution Language) BPEL Process is a language used for the composition, orchestration and coordination of webservics. In this post we will explain BPEL, define the BPEL role with regard to Service Oriented Architecture and explain the process-oriented approach to SOA and the role of BPEL.
In BPEL the Enterprise application and information systems have become more more fundamental assets to companies. The Companies are trust on them to be able to perform business operations.
Enterprise Information system can improve the efficiency of businesses through the automation of business processes. The objective of almost every company is that the application it uses should provide comprehensive support for business processes. It means that applications should align with business processes closely.
BPEL Role of business processes and their challenges,BPEL Business and IT alignment,What are BPEL features,what are BPEL features, BPEL Orchestration and Choreography, Examine the relation of BPEL to other Languages, The future of BPEL.
Already existing applications have often been developed using older technologies, languages and architectures, which are by definition less flexible to change. Such C,C++, and Mainframe. These applications are tightly coupled applications, constructed of interrelated modules, these are can not be differentiated, upgraded, or refactored with reasonable amount of effort, place important limitations on the flexibility of such applications.
Already existing applications are also difficult to modify and adapt because they have not been developed in a flexible way that would allow modifying application parts quickly and efficiently. Modifying existing applications are require more time Complexity of existing applications and the overall IT Architecture, Modifying them is a complex, difficult and time-consuming task.
Question 42. What Are Predefined Errors In Bpel?
Answer :
Custom errors
Timed out errors
BPM errors
Validation Errors
Question 43. How Can You Increase Performance In Bpel?
Answer :
We can increase the performance by writing indexes and sequences. (Or) Go to application server - Configurations - Change Xml file
Question 1. What Is Soa ?
Answer :
SOA stands for Service Oriented Architecture. SOA is not any tool, rather is a concept and there are many tools in the market based upon this concept. In this SOA Concept, we use SOA layer as middle or intermediate layer between services so that these service can communicate with each other.
Question 2. Benefits Of Soa ?
Answer :
Below are the major benefits that we get from SOA.
Loose Coupling : This means that the service requester has no knowledge of the technical details of the provider’s implementation, such as the programming language, deployment platform, and so forth. The service requester typically invokes operations by way of messages — a request message and the response — rather than through the use of APIs or file formats.
Cost Cutting
Better reuse: Build new client functionality on top of existing Business Services.
Well defined interfaces: Make changes without affecting clients
Easier to maintain : Changes/Versions are not all-or-nothing
Better flexibility
Question 3. What Is Oracle Soa Suite Tool ?
Answer :
SOA Suite tool is a middleware tool from Oracle which is based upon SOA concept comes under Oracle Fusion Middleware stack. We use this tool for integration purpose .i.e. This tool is used to integrate two system/applications etc.
Question 4. Is Oracle Soa Suite Tool State Full ?
Answer :
Yes SOA Suite tool is a state full tool, that means in this tool we store every state in database i.e. we store all the incoming messages, transformed messages, outgoing messages to database along with timestamp.
Question 5. How Many Components We Have In Oracle Soa Suite Tool?
Answer :
We have total 5 components in Oracle SOA Suite tool as mentioned below.
BPEL : Business Process Execution Language
Mediator
Business Rules
Human Task
Spring
Question 6. What All Components/products Needs To Be Installed Before We Install Oracle Soa Suite Tool ?
Answer :
Following components needs to be installed before we install Oracle SOA Suite.
JDK
Database
All Required Schema (Created using RCU)
WebLogic Server
Question 7. Which Application Server Required For Oracle Soa Suite Tool ?
Answer :
Mostly WebLogic server is used as application server for Oracle SOA Suite tool.
Question 8. Which Ide We Use For Oracle Soa Suite Tool ?
Answer :
We use JDeveloper IDE for Oracle SOA suite tool.
Question 9. What Is Domain ?
Answer :
A domain is the basic administration unit for WebLogic Server instances. i.e. Domains include a special WebLogic Server instance called the Administration Server, which is the central point from which you configure and manage all resources in the domain.
Question 10. What Is Administration Server ?
Answer :
A domain has one WLS instance configured as an admin server. The admin server provides a central point for managing a domain.
Question 11. What Is Managed Servers ?
Answer :
All other WLS instances in a domain are called Managed Servers. Managed servers host application components and resources.
Question 12. What Is Cluster ?
Answer :
Cluster is a group of server instances that work together as a single runtime unit from a client perspective. Clustering provides scalability and high availability for applications.
Question 13. What Is Em ?
Answer :
EM stands for Enterprise Manager. It is webpage we deploy, test, monitor, diagnose and resolve problem for composites. It is hosted on the Admin Server.
Question 14. What Is Soa-infra ?
Answer :
soa-infra is a J2EE application that is targeted to either a managed server or a cluster. All the composites gets deployed under soa-infra application.
Question 15. What All Schema We Need For Oracle Soa Suite Tool ?
Answer :
We require following schema.
MDS – This schema is used to store all the artifacts like WSDL, XML, XSD etc.
SOA_INFRA – This schema is used to store SOA Component Engine properties, deployed composites, payloads, runtime metadata etc.
ORABAM – This schema is used to store the metadata that is related to BAM and its components and this is optional schema.
ORASDPM – This schema is used to store metadata about the user messaging systems.
Question 16. What Is Partition ?
Answer :
Sections of the SOA Infrastructure where we deploy SOA composite applications known as partition. When we install SOA suite tool, default partition get created with name “default” but we can add as many as partitions as required.
Question 17. What Are Benefits Of Partition?
Answer :
Below are the major benefits of partition.
Logically group SOA composites.
Perform bulk lifecycle management tasks on large numbers of composites.
Question 18. What All Bulk Operations We Can Perform On Partition ?
Answer :
We can perform below operations.
Start all composites
Shut down all composites
Undeploy all composites
Retire all composites
Activate all composites
List all composites
Question 19. How We Can Deploy Composite To Soa Server ?
Answer :
There are different methods to deploy SOA composite to SOA server.
Through EM console
Directly from JDeveloper
Scripting (Ant, WLST etc.)
Question 20. What Is Config Plan ?
Answer :
Config plan is used during composite deployment. This is a xml file where we specify the parameters that we want to replace while doing the deployment to next environment.
Question 21. Can We Have Multiple Composites With Same Name On Soa Server ?
Answer :
Yes, we can have multiple composites with same name on SOA server but this is possible when we have composites with revisions.
Question 22. If We Have Multiple Composites On Soa Server With Same Name Then How Composites Run ?
Answer :
If we have multiple composites with same name then only one composite will act as default composite which will run only. But we can go to EM console and make other composite default.
Question 23. What Role Does Zookeeper Plays In Hbase?
Answer :
HBase comes integrated with Zoo keeper. When I start HBase, Zoo keeper instance is also started. The reason is that the Zoo keeper helps us in keeping a track of all region servers that are there for HBase. Zoo keeper keeps track of how many region servers are there, which region servers are holding from which data node to which data node. It keeps track of smaller data sets where Hadoop is missing out. It decreases the overhead on top of Hadoop which keeps track of most of your Meta data. Hence HMaster gets the details of region servers by actually contacting Zoo keeper.
Question 24. What Is Memstore ?
Answer :
The MemStore is a write buffer where HBase accumulates data in memory before a permanent write.
Its contents are flushed to disk to form an HFile when the MemStore fills up.It doesn’t write to an existing HFile but instead forms a new file on every flush. There is one MemStore per column family.
Question 25. What Is Wal ?
Answer :
We cannot be sure that the data will be persistent throughout in Memstore. Assume that a particular datanode is down. Then the data that resides on that data node’s memory will be lost.
To overcome this problem, when the request comes from the master it written to WAL as well. WAL is nothing but Write Ahead Logs which resides on the HDFS, a permanent storage. Now we can make sure that even when if the data node is down the data will not be lost I.e. we have the copy of all the actions that you are supposed to do in the WAL.
Question 26. What Are The Two Types Of Table Design Approach In Hbase?
Answer :
They are − (i) Short and Wide (ii) Tall and Thin
Question 27. Benefits Of Sca ?
Answer :
Easier Development :No need to write lengthy code as we get all components prebuilt.
Easily compose a assembly (composite) by just linking different these prebuilt components.
Better re-usability
Question 28. What Is Soa Composite ?
Answer :
SOA composite is a assembly comprises of one or more than one pre-build components. In SOA composite we wires different components together to perform required business functionality.
Question 29. What Is Service Component ?
Answer :
All prebuilt components BPEL , Mediator, Business Rules, Human Task and Spring known as service components.
Question 30. Can We Have More Than One Service Component In One Composite ?
Answer :
yes, we can have as many as service components in one composite but it is not recommended, we should not have all the components in one composite itself.
Question 31. How These Service Components Works ?
Answer :
Each service component is hosted in its own service engine container. E.g. Any logic added in BPEL components will be handled by BPEL service engine only.
Question 32. What Is Binding Component ?
Answer :
As name suggest, this component is used to bind composite application to external world. i.e. we use these components to link composite with source and target system.
Question 33. What Are The Types Of Binding Components ?
Answer :
Binding components are of two types as mentioned below.
Service Binding : With the help of this binding we connect composite to source or client system or we can say this is entry point of composite.
Reference Binding: This binding helps composite to connect to target or reference systems or we can say it is exist point of the composite.
Question 34. Can We More Than One Service & Reference Binding In One Composite ?
Answer :
Yes, we can more than one service & reference binding in one composite, that means we can have more than one entry & exist point for composite.
Question 35. What Can Be Scenario Where We Have Two Service Binding In One Composite ?
Answer :
When a composite can be initiated either by direct call or by consuming the same message from JMS queue, in this scenario we have two entry point for same composite.
Question 36. What Can Scenario Where We Have Two Reference Binding In One Composite ?
Answer :
Composite needs to send the message to first target by JMS queue and to other target by writing the file, in this scenario we have two exist for composite.
Question 37. What Is Wire ?
Answer :
Connection between service & binding component and within service & binding components know as wire. I.e. This enable us to graphically connect the components in a SOA composite application.
Question 38. What Is Bpel ?
Answer :
BPEL stands for Business Process Execution Language, it is one of the component of SOA Suite tool. BPEL is a XML based language used to design business process/flows. We perform service orchestration in BPEL.
Question 39. What Are Different Parts Of Bpel ?
Answer :
Below are different parts of BPEL as mentioned below.
Service Interface: A WSDL describing the functionality of the BPEL process. The service interface provides the end user a way to interact with the BPEL process component using Service Interface / Service Binding.
Activities: units of work. The actual elements that make up the BPEL process flow or sequence of instructions to be executed.
Partner links: also called Reference bindings. A partner link describes the roles played for the interaction between the BPEL process and the service it invokes.
Question 40. What All Bpel Templates Are Available In Soa Suite Tool ?
Answer :
Primarily we have three types of BPEL template in SOA Suite tool.
Synchronous BPEL Template
Asynchronous BPEL Template
OneWay BPEL Template
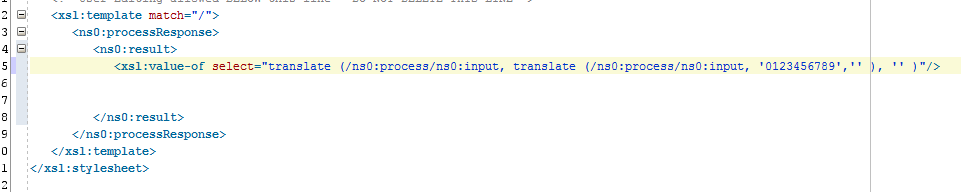


Comments
Post a Comment